Shockwave Therapy
Why Shockwave Therapy?
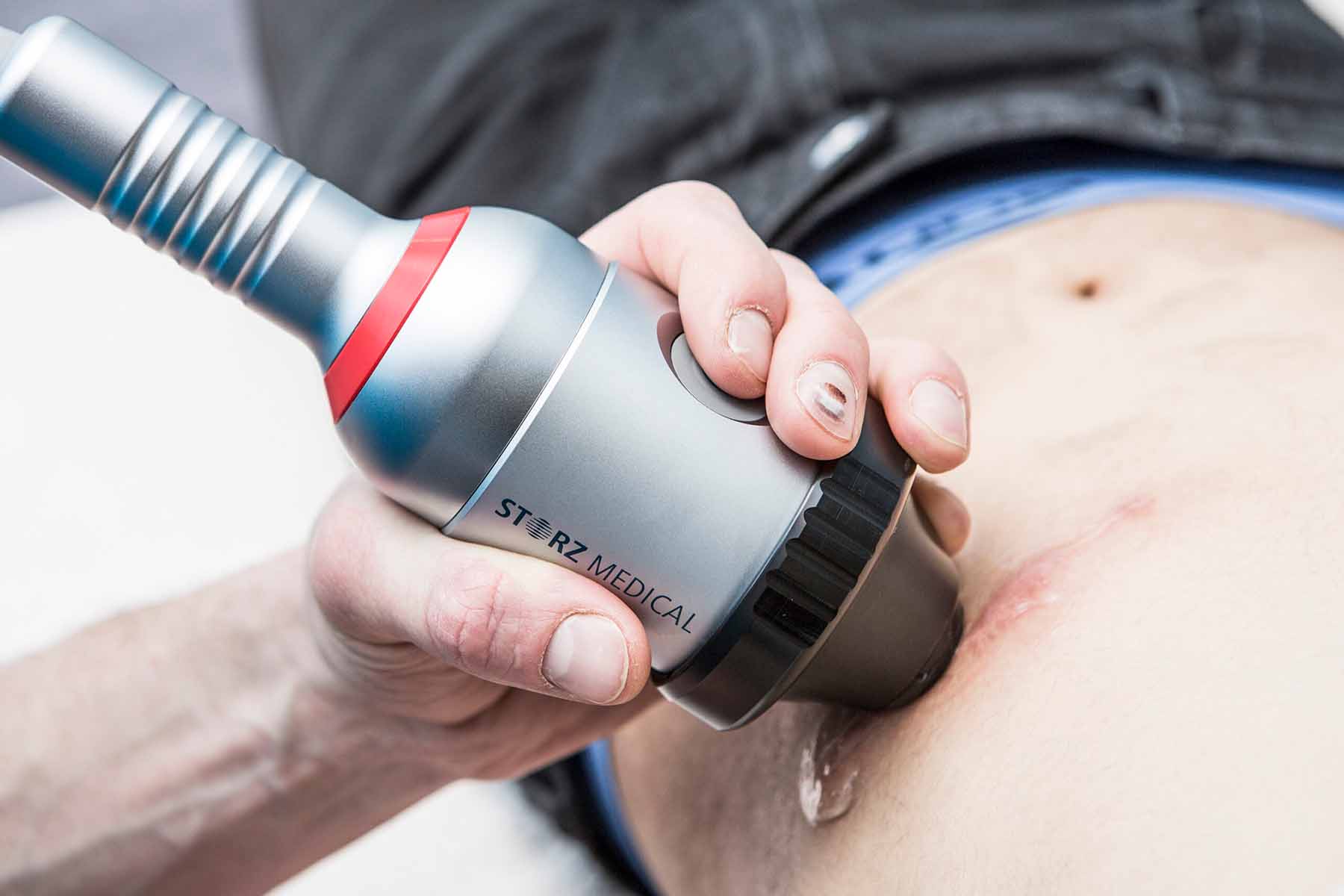
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) is a type of pulsed acoustic wave resulting from excessive pressure changes. It has been used to treat musculoskeletal diseases (plantar fasciitis, lateral epicondylitis of the elbow, etc.) and wounds. Recent research has shown that ESWT is effective in stimulating biological activities that involve cellular activity. These results suggest that ESWT improves blood perfusion and can be used in tissue regeneration/ scar remodelling. Shockwave treatment is performed without anaesthesia; a treatment head and gel are applied to the area of scar treated.
Working mechanism
Shockwave works by the translation of acoustic energy into mechanical stimulation or physical energy. This encourages biological responses which promote repair of compromised tissue via complex molecular and cellular interactions and changes. The effect of shockwave therapy is dose-dependent; treatments at low intensity seem best for burn scars. Higher intensity treatments can reduce scar growth and are better for keloid/hypertrophic scars. ESWT is non-invasive and safe, it can be used within the first three months of wound healing when the scar is still fragile.
Main improvements
- Improved elasticity of the tissue (and increased range of movement)
- Improved pigmentation
- Improved scar height
- Tissue regeneration and remodelling
- Quicker wound healing
Adverse effects
Reported adverse effects:
- Slight pain sensation during treatment
- Itching sensation during treatment
F.A.Q.